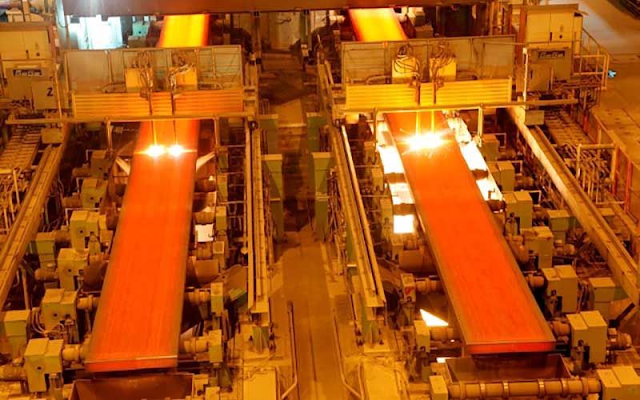
Hot Rolling Process
The semi-finished billet from the steel plant is rolled to make it a qualified product.
Introduction of hot polling process
Process Flow of Hot Rolling: Process Flow of Main Rolling Mill Line:
The slab is directly sent to the slab warehouse of the hot rolling workshop from the slab discharging roller table of the continuous caster in the steelmaking and continuous casting workshop, and the directly hot charged slab is sent to the furnace loading roller table of the reheating furnace for heating.
The slab that cannot be directly hot charged is lifted into the insulation pit by the crane, and then lifted to the upper material bench by the crane after insulation, and then heated by the furnace loading roller table of the heating furnace, leaving the possibility of direct rolling.
The continuous casting slab is transported into the slab warehouse by the continuous casting workshop through the slab loading roller table or slab unloading roller table.
Before the slab reaches the entry point, the technical data about the slab has been sent to the computer system of the hot rolling plant by the computer system of the continuous casting workshop, and the relevant data of the slab is displayed on the monitor, so that the staff can check and receive the defect free and qualified slab.
In addition, the cleaned slab also needs to be checked, accepted and input into the computer. The flow direction of slabs entering the slab warehouse shall be determined by the slab warehouse computer management system according to the rolling plan.
Conventional slab charging and rolling: after the slab enters the slab warehouse, the slab is stacked to the designated stacking position in the slab warehouse by the slab clamp crane according to the unified instruction of the slab warehouse control system. During rolling, according to the rolling plan, the slab is lifted out of the stack one by one by the slab clamp crane, and lifted to the slab loading bench for loading.
The slab is weighed and checked by the weighing roller table, and then sent to the furnace loading roller table of the heating furnace. After the slab is measured and positioned, it is loaded into the heating furnace by the steel loader for heating.
Hot charging and rolling of carbon steel insulation pit: after the slab enters the slab warehouse, the slab is stacked to the designated stacking position in the insulation pit by the slab clamp crane according to the unified instruction of the slab warehouse control system.
During rolling, according to the rolling plan, the slab is taken out of the insulation pit one by one by the slab clamp crane, lifted to the slab loading bench for loading. The slab is weighed and checked by the weighing roller table, and then sent to the furnace loading roller table of the heating furnace.
After the slab is measured and positioned, it is loaded into the reheating furnace by the steel loader for heating.
Direct hot charging and rolling: when the production plans of continuous casting and hot rolling match, the qualified high-temperature continuous casting slab is transported to the weighing roller table through the charging roller table of the heating furnace.
After weighing and checking, it enters the charging roller table of the reheating furnace.
After the slab is measured and positioned in front of the designated reheating furnace, it is loaded into the reheating furnace by the charging machine for heating.
Some of the directly hot loaded slabs transported through the unloading roller table need to be lifted by a crane once, placed on the loading roller table and directly sent to the reheating furnace area.
If the steel-making plant can realize the direct hot charging and the slab is transported by the feeding roller table, some crane lifting operations can be reduced.
After the slab is sent to the heating furnace through the charging roller table of the reheating furnace, it is loaded into the heating furnace by the supporting machine.
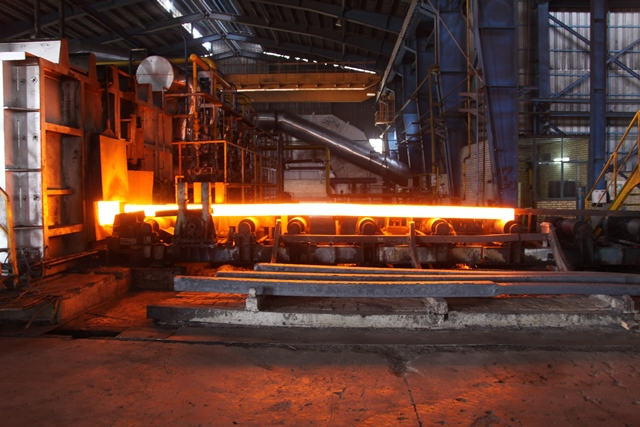
After heating to the set temperature, it is supported by the tapping machine according to the rolling rhythm and placed on the discharging roller table of the reheating furnace.
After the heated slab is discharged from the furnace, it is transported through the conveying roller table. After descaling by the high-pressure water descaling device, the slab is sent to the fixed width press for side pressing and fixed width as required. The maximum one-time width reduction of the fixed width press is 350mm.
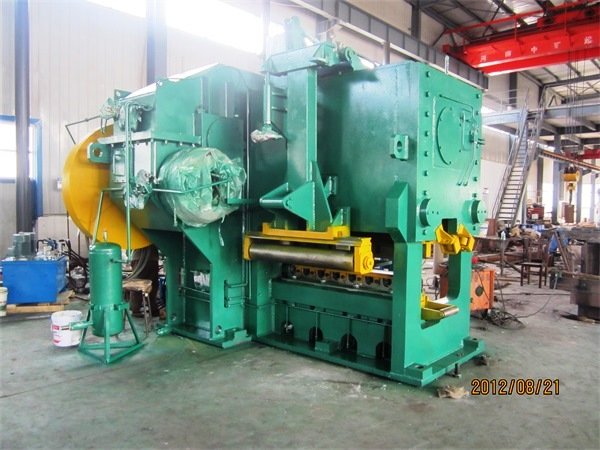
Then it is transported by the roller table into the first two high reversible roughing mill and the second four high reversible roughing mill. The slab is rolled into an intermediate slab with a thickness of about 30-60mm according to the process requirements.
The vertical roll mill in front of each roughing mill can control the width of the intermediate billet.
An intermediate waste billet pushing device is arranged between R2 and the flying shear to push the intermediate waste billet onto the operation side bench of the intermediate roller table.
The intermediate billet is transported by the intermediate roller table with thermal insulation cover to the cutting head and tail of the flying shear. The thermal insulation cover is conducive to reducing the heat loss of the intermediate billet and the temperature difference between the head and tail of the belt billet.
An edge heater is set in front of the flying shear, which can reduce the temperature difference between the edge and the middle part of the intermediate billet, improve the uniformity of strip steel performance and improve the quality of rolled piece shape.
The cutting head flying shear is equipped with an intermediate blank head and tail shape detector and a cutting optimization control system to realize optimal cutting and reduce the loss of cutting head and tail.
The strip blank after head cutting is removed from the secondary iron oxide scale by the high-pressure water descaling device before finishing rolling, and is guided into the finishing rolling unit by the vertical roll before finishing rolling.
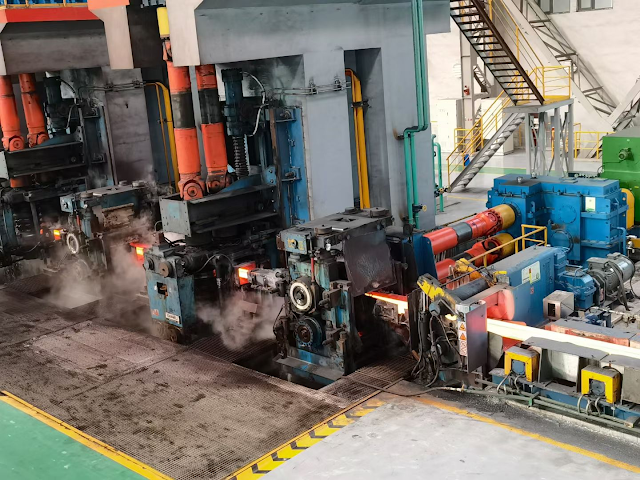
The intermediate billet is rolled into 1.2 ~ 25.4mm finished strip by F1 ~ F7 four roll finishing mill.
The threading speed, acceleration, maximum rolling speed, reduction of each stand, roll shifting stroke of work roll and roll bending force of each stand of the finishing mill are calculated and set by the computer control system according to the variety and specification of rolled strip to realize the closed-loop control of strip shape.
In order to effectively control the quality of strip steel, the rolling line detection instruments such as crown, flatness, thickness, width and temperature are set at the outlet of F7 finishing mill, and the rolling line detection instruments such as strip surface quality, width and temperature are set at the inlet of coiler.
The strip rolled by the finishing mill is cooled from the final rolling temperature to the specified coiling temperature by the strip laminar cooling system on the output roller table.
The cooling water volume is set and calculated by the computer according to the steel strip cooling mode and final coiling temperature.
When the coiler passes through the strip before biting into the strip, the speed of the output roller table, pinch roll, auxiliary roll and drum is ahead of the rolling speed of the final frame;
When the strip steel is bitten by the coiler, the output roller table, pinch roll and coiler will conduct speed-up rolling synchronously with the finishing mill;
When the tail of the strip steel leaves the end frame, the output roller table and pinch roller shall slow down, that is, lag behind the coiling speed of the coiler until the tail of the hot rolled coil.
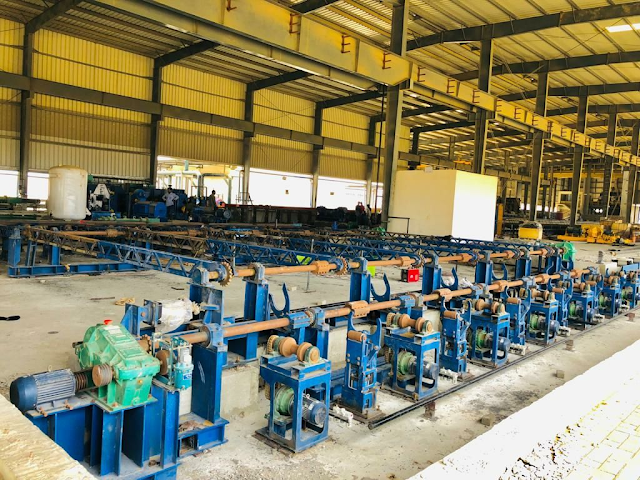
After coiling, the steel coil is lifted out by the coil unloading trolley to the baler for bundling. Then the steel coil is transported backward by the steel coil transportation system.
After baling, weighing and marking, it is transported to the hot-rolled steel coil finished product warehouse, cold-rolled raw material warehouse and finishing raw material warehouse respectively.
After the steel is returned to the hot rolling and coiling warehouse for inspection, the raw materials that need to be transported to the hot rolling and coiling warehouse for inspection are sent to the hot rolling and coiling warehouse for inspection, and the finished products are sent to the hot rolling and coiling warehouse for inspection respectively.
The steel coils cooled in the steel coil warehouse shall be sent to the leveling and winding unit, steel plate cross cutting unit, cold rolling workshop or delivered according to the sales plan according to the next processing process requirements. The steel coil is transported and stacked in the way of horizontal coil.
The transportation system for the steel coil to the steel coil warehouse or cold rolling raw material warehouse adopts the pallet transportation system, and forms a transportation network together with the transportation system of 1780 hot rolling plant, which is uniformly controlled by the computer.
From the slab entering the slab warehouse to the delivery of finished products, the whole process tracks the slab, rolled piece and coil through the rolling line material tracking system and two warehouse management system, so as to realize the automatic production control of computer.
Please contact stella@hanrm.com for a quotation.
And free send inquiry to us.
Email: stella@hanrm.com stellarollingmill@gmail.com
Whatsapp/Wechat:+8615877652925